download api-ms-win-crt-heap-l1-1-0.dll install, register, regsvr32 for windows 8.1,10,7,xp, vista,32-bit

download api-ms-win-crt-heap-l1-1-0.dll install, register, regsvr32 for windows 8.1,10,7,xp, vista,32-bit
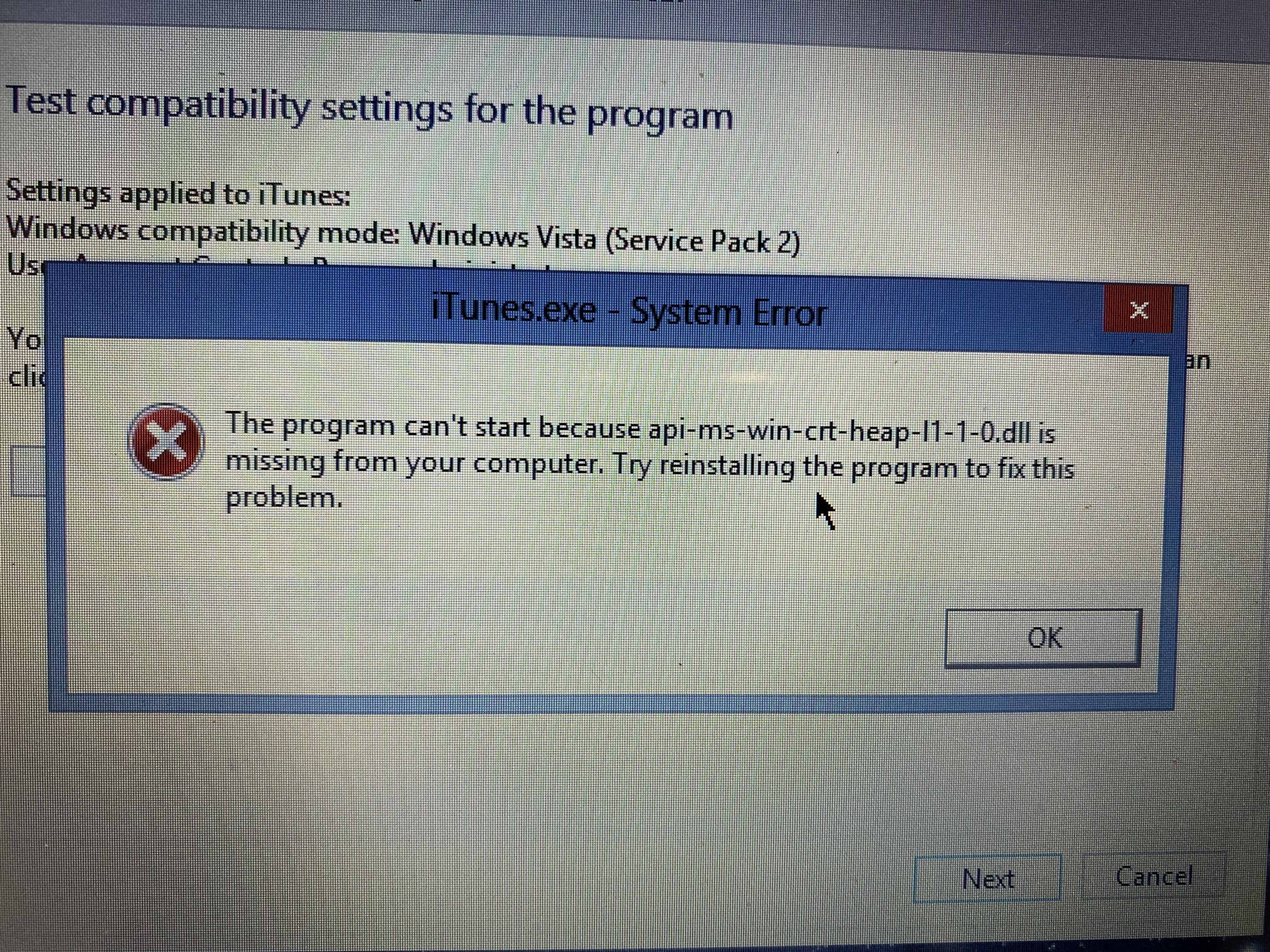
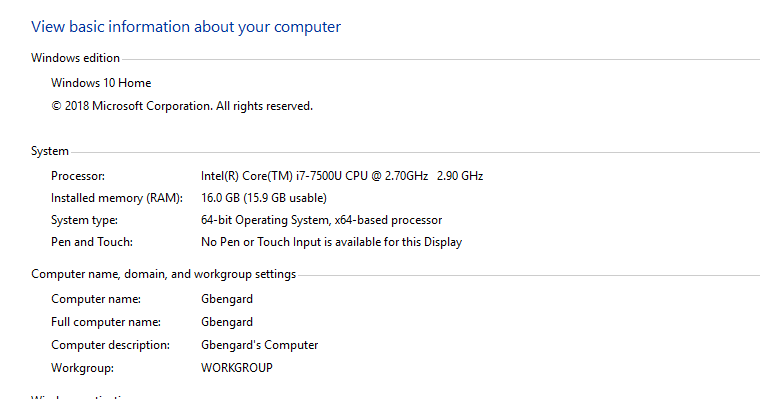
I haven't used my computer in a while. Now that I'm trying to backup my old iPhone and restore into my new one any time I try opening iTunes I get this

download api-ms-win-crt-heap-l1-1-0.dll install, register, regsvr32 for windows 8.1,10,7,xp, vista,32-bit

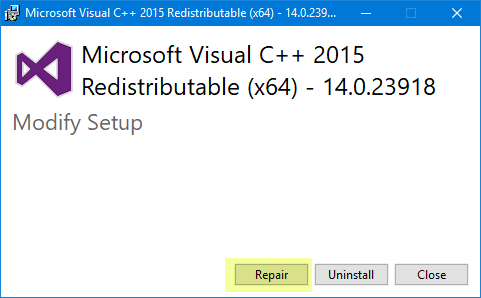
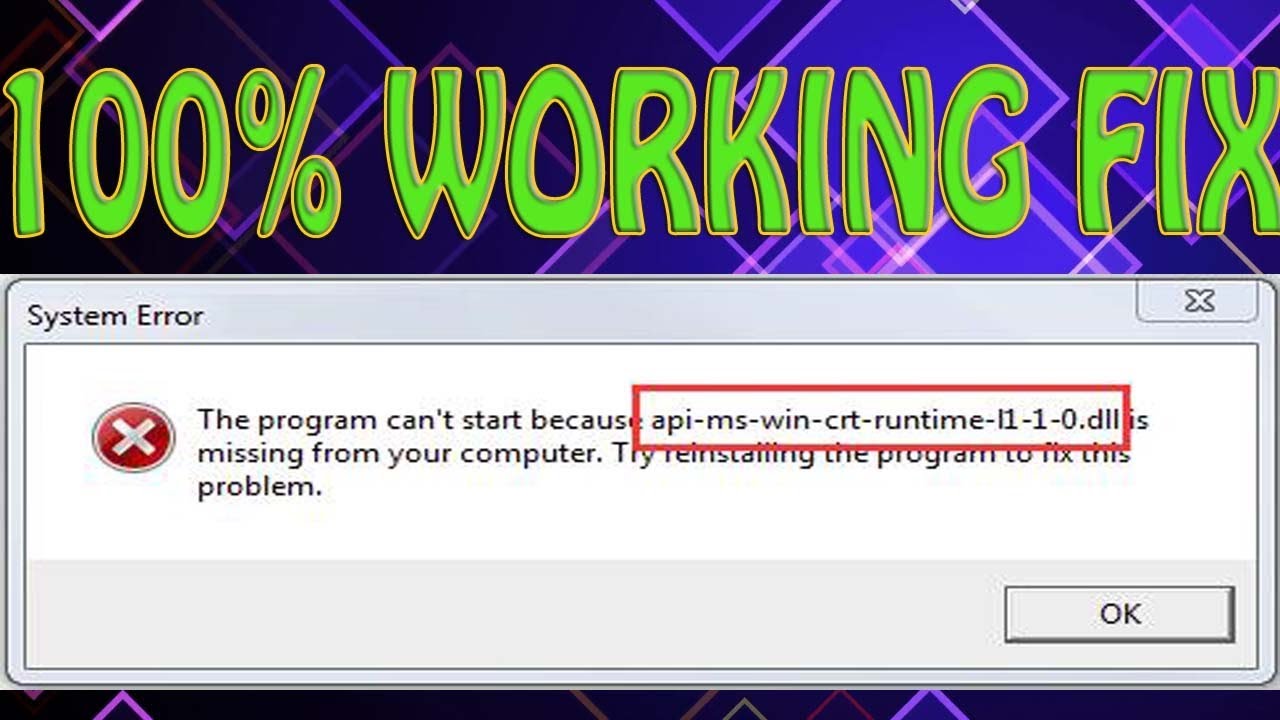
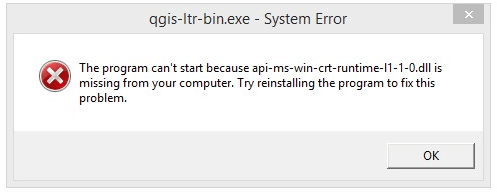
How to Fix api-ms-win-crt-runtime-l1–1–0.dll is Missing from Your Computer Error? | by Zaynwilder | Medium
Computer running slow, pages loading slowly, wasnt like that before. - Page 4 - Virus, Spyware, Malware Removal


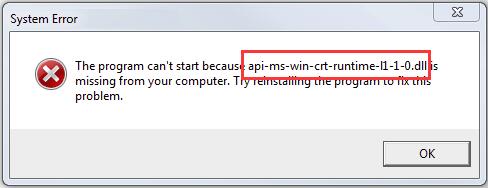





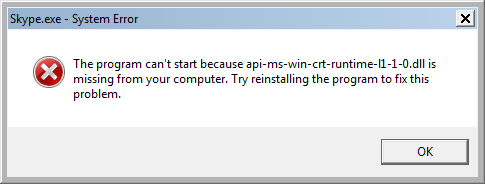
![FIX ITunes Error api-ms-win-crt-runtime-l1-1-0.dll is Missing [UPDATED] - YouTube FIX ITunes Error api-ms-win-crt-runtime-l1-1-0.dll is Missing [UPDATED] - YouTube](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/odi-F29yKTI/maxresdefault.jpg)