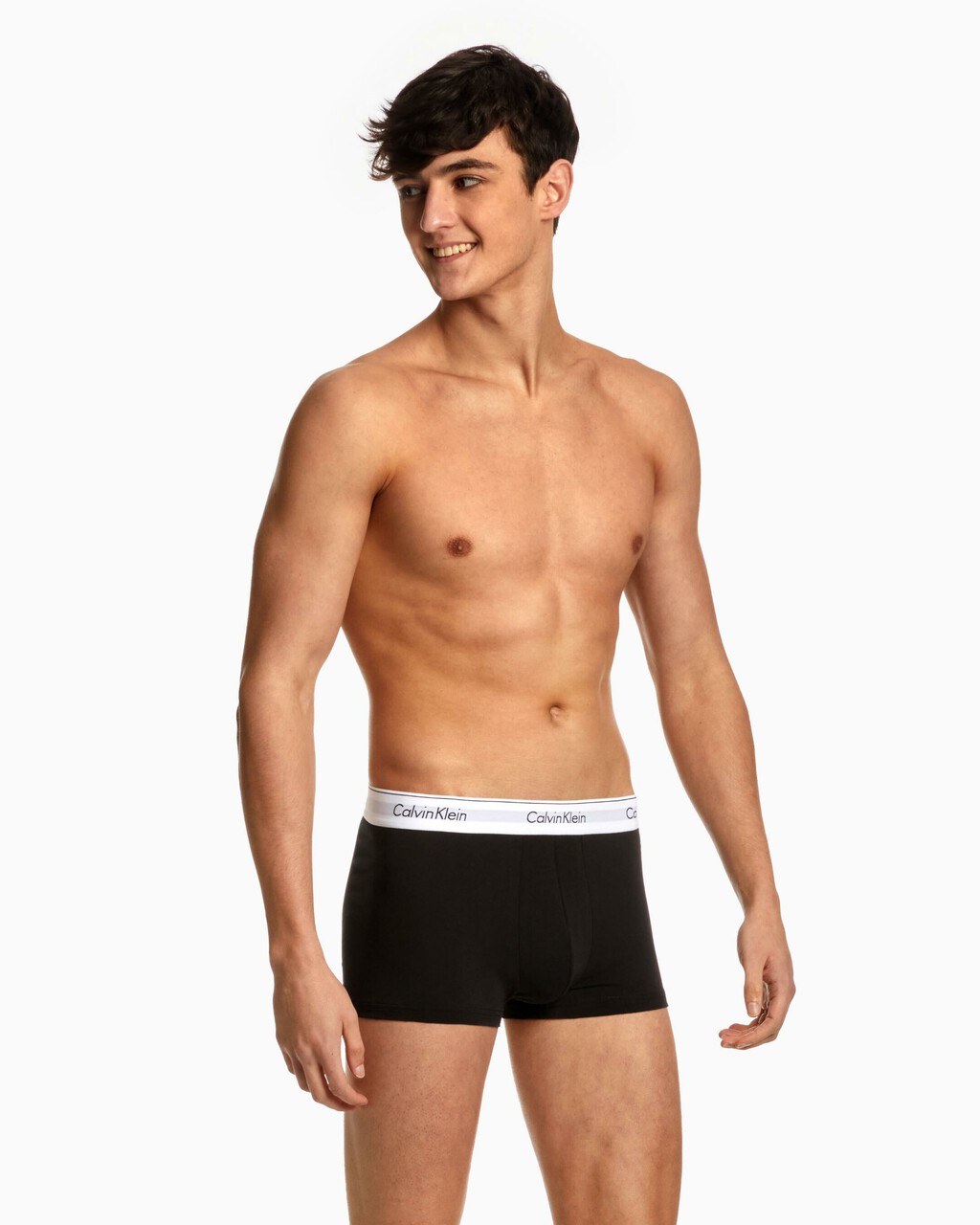
S/M) Calvin Klein 2-pack Modern Cotton Stretch Low Rise Trunk Men Underwear, Men's Fashion, Bottoms, New Underwear on Carousell
:fill(ffffff)/https://static-hk.zacdn.com/p/calvin-klein-4825-5110836-1.jpg)
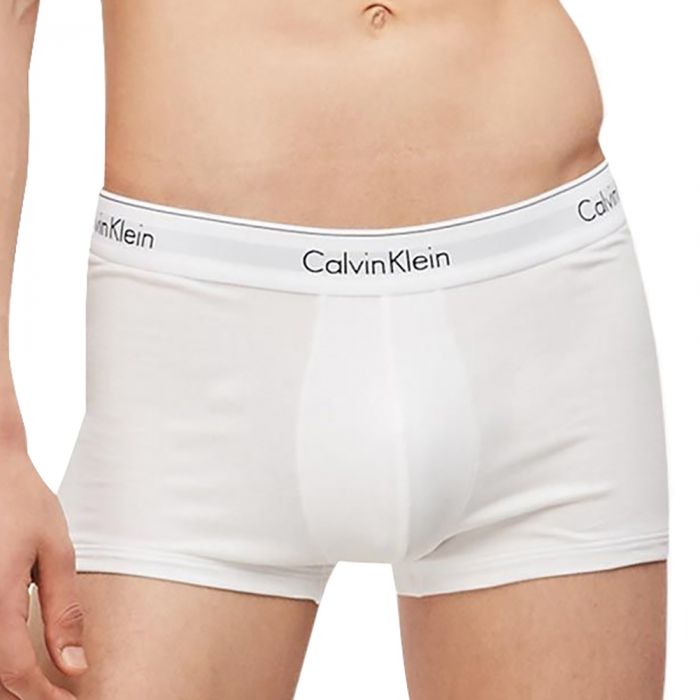
Calvin Klein Modern Cotton Stretch Trunks 2 Packs - Calvin Klein Underwear 2023 | Buy Calvin Klein Online | ZALORA Hong Kong
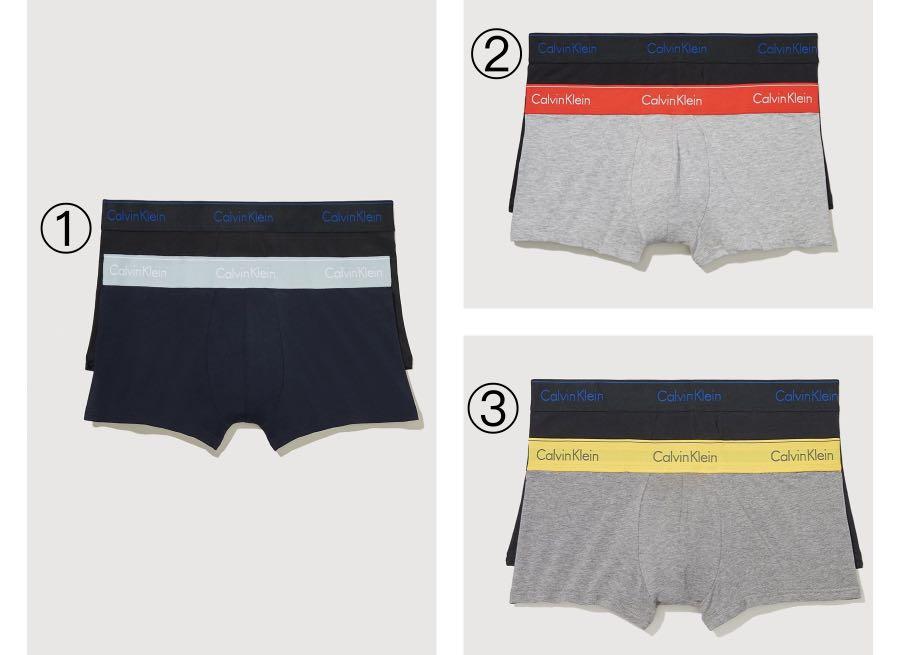

S/M) Calvin Klein 2-pack Modern Cotton Stretch Low Rise Trunk Men Underwear, Men's Fashion, Bottoms, New Underwear on Carousell

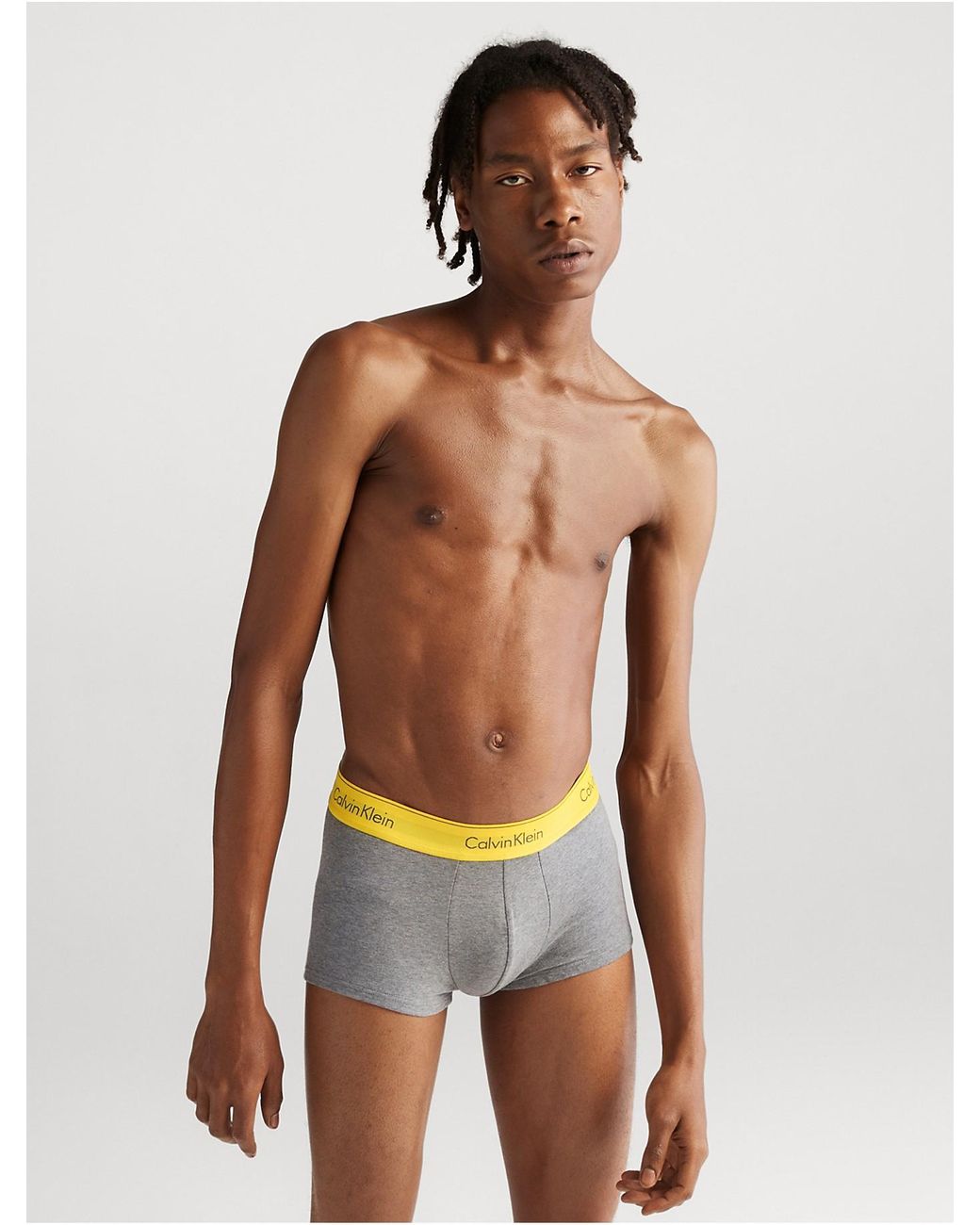
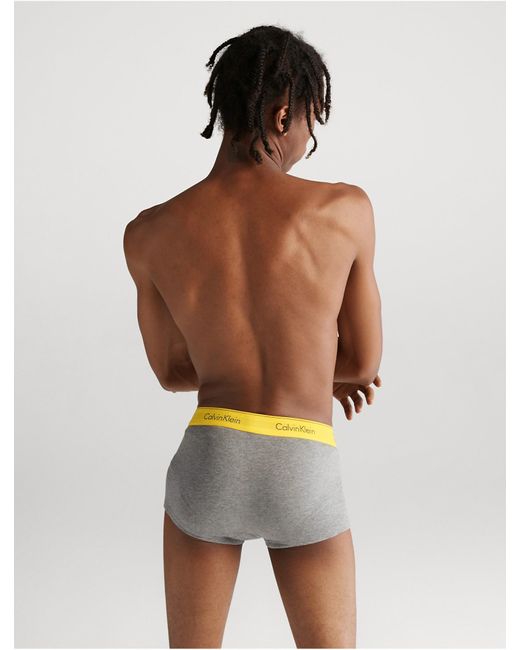
Amazon.com: Calvin Klein Men's Modern Cotton Stretch Naturals 3-Pack Low Rise Trunk, Sandalwood, Cedar, Black, Small : Clothing, Shoes & Jewelry
Calvin Klein Men's 3-Pack Cotton Stretch Low-Rise Trunks & Reviews - Underwear & Socks - Men - Macy's
:fill(ffffff)/https://static-hk.zacdn.com/p/calvin-klein-1902-0599736-1.jpg)
Calvin Klein Modern Cotton Stretch Trunks 2 Pack - Calvin Klein Underwear 2023 | Buy Calvin Klein Online | ZALORA Hong Kong



















