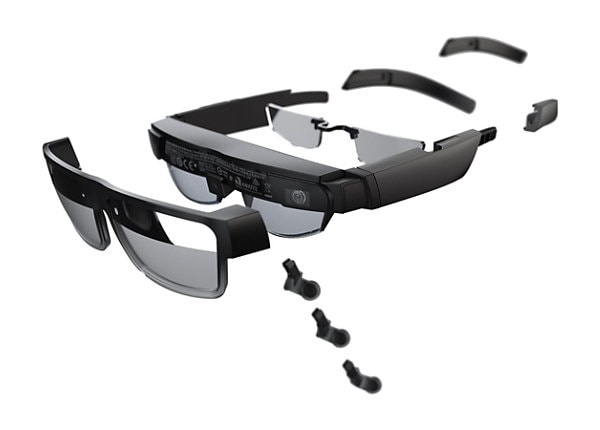
Realmax Dry Eye Smart Ar Glasses Wear Smart Glasses Hd Projection Immersive Head Display - All-in-one Vr - AliExpress

Smart Glasses Screen Display | Video Smart Glasses Display | Rokid Air Accessories - Vr/ar Glasses Accessories - Aliexpress

Grawoow G350 Smart Glasses 3d Movie Augmented Reality Head Display Non-vr - All-in-one Vr - AliExpress
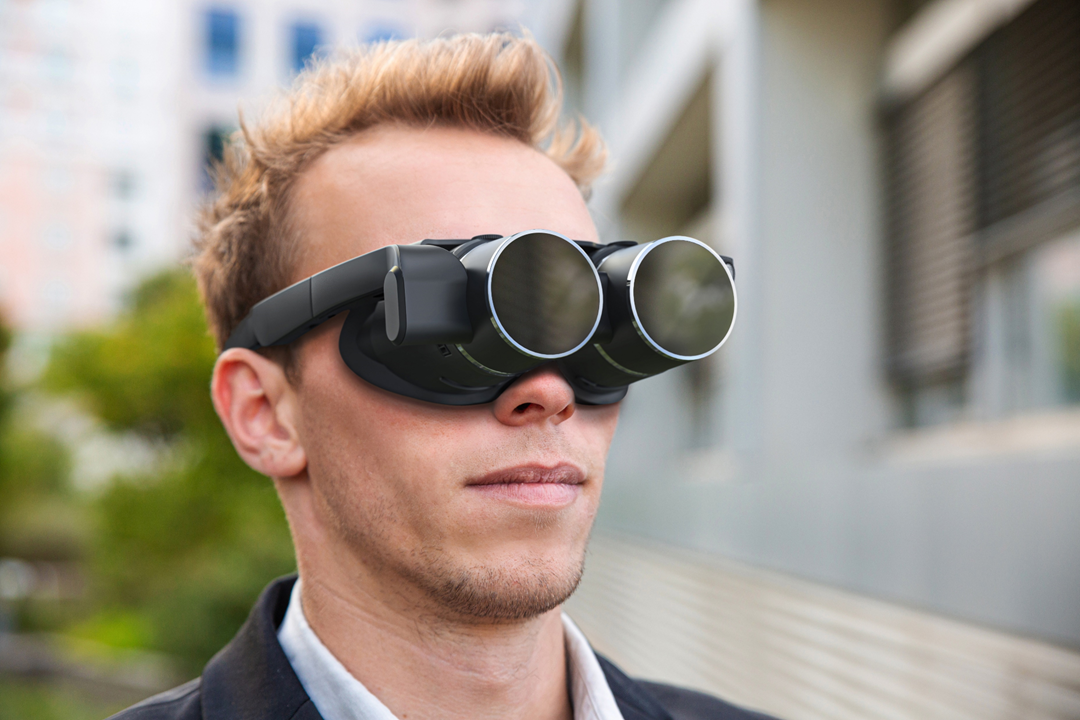

Biel Glasses and Panasonic demonstrate Life-Changing Smart Glasses for the Visually Impaired at CES 2023 | Others | Products & Solutions | Blog Posts | Panasonic Newsroom Global

Smart glasses, VR virtual reality, and AR augmented reality technology. Smart glasses with futuristic technology graphics and modern city background Stock Illustration | Adobe Stock

VR Smart Glasses 360 Degree Panoramic Mobile Phone 3D Virtual Reality Headset Box Google Game Helmet for 4.7 7.0" Smartphone| | - AliExpress

Rokid Air Ar 3d Glasses Foldable Vr Smart Glasses 120" Screen 1080p Oled Dual Display 43°fov 55ppd Home Game Viewing Device - Photo Studio Kits - AliExpress
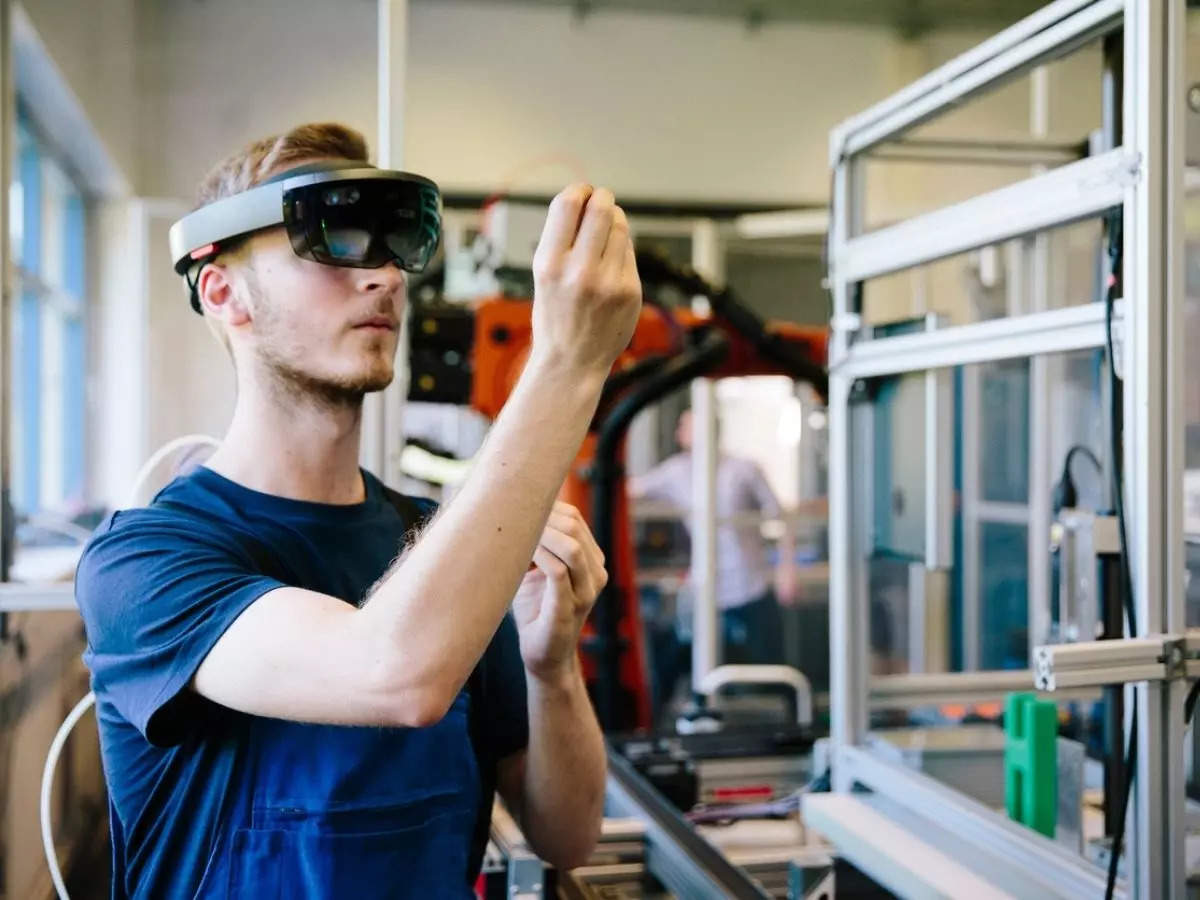

Smart glasses, VR headsets: The face computer is coming ... but is the world ready for it?, ET BrandEquity
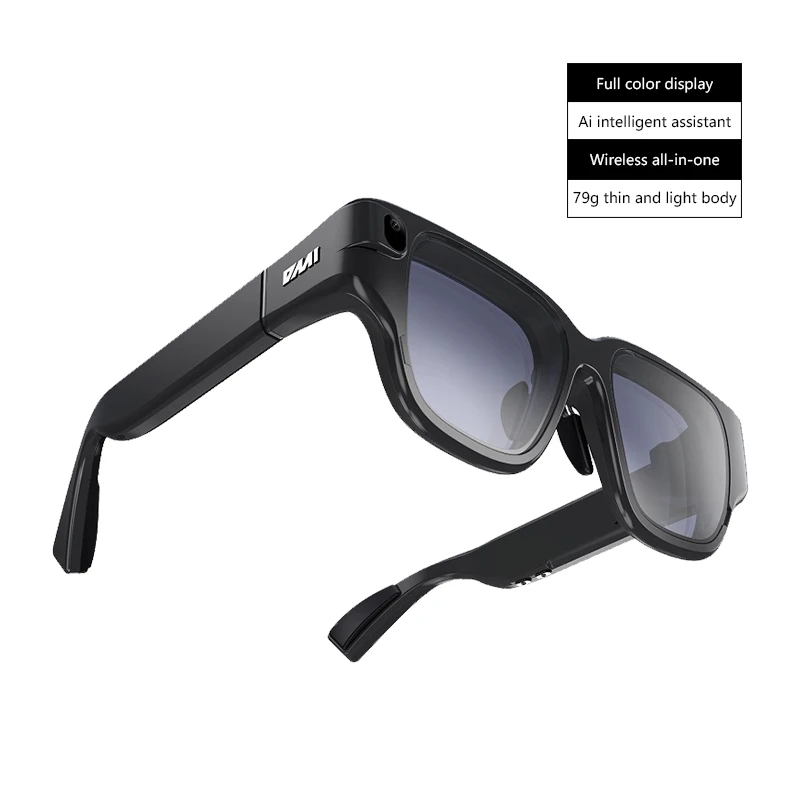

High Quality Smart Ar Glasses Smart Glasses Ar Vr Gaming Smart Glasses - Buy Smart Ar Glasses,Smart Glasses Ar,Vr Gaming Smart Glasses Product on Alibaba.com

2022 New Smart Headset Virtual Reality Glasses Vrg Pro Audio Video Version All-in-one Mobile Phone 3d Vr Glasses - Buy Guangdong Vr Glasses,Phone Vr Glasses,Vr Smart Glasses Product on Alibaba.com

Amazon.com: Nreal Air AR Glasses, Smart Glasses with Massive 201" Micro-OLED Virtual Theater, Augmented Reality Glasses, Watch, Stream, and Game on PC/Android/iOS–Consoles & Cloud Gaming Compatible : Cell Phones & Accessories

Virtual Reality Vr 3d Imax Glasses | Videos Imax 3d Glasses | Glasses Shine Vr | Vr 3d Hd - Pc Vr - Aliexpress

INMOLENS AR VR Glasses Smart Glasses INMO Air Teleprompter Cycling Navigation Mobile Phone Wireless Projection Lightweight| | - AliExpress

Amazon.com: Nsxcdh 3D VR Smart Glasses - 3D VR Virtual Reality Goggles Headsets for Video Movies & Games for Kids & Adults Wireless Bluetooth Compatible with Android/iOS/PC(White) : Cell Phones & Accessories
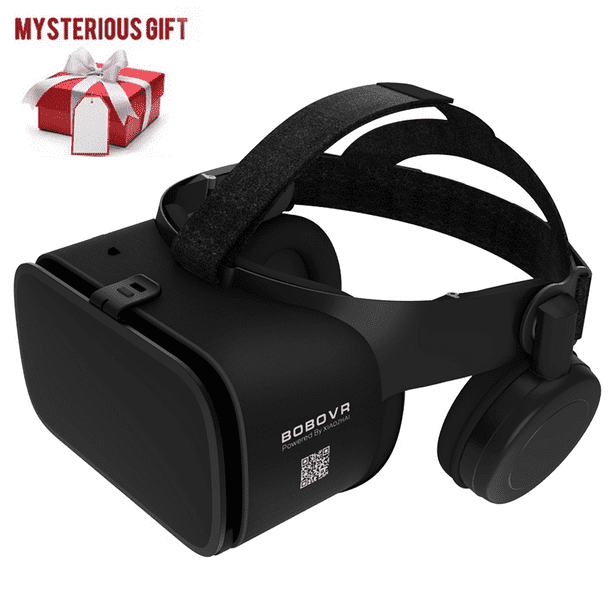

2023 Virtual Reality 3D VR Headset Smart Glasses, with Wireless Remote Control, VR Glasses for IMAX Movies & Play Games , Compatible for Android iOS System, Comfortable, with Mystery Gift - Walmart.com