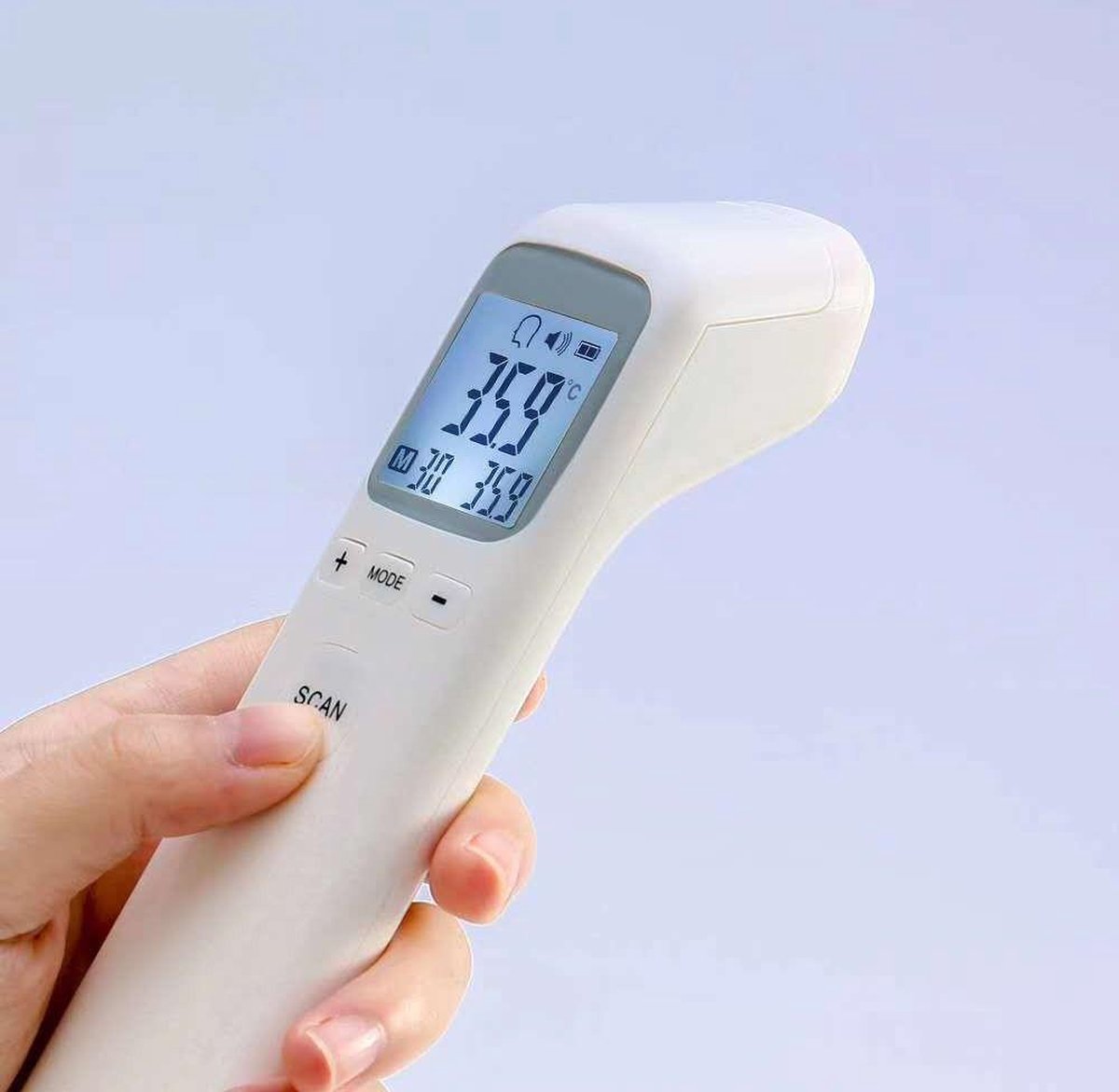
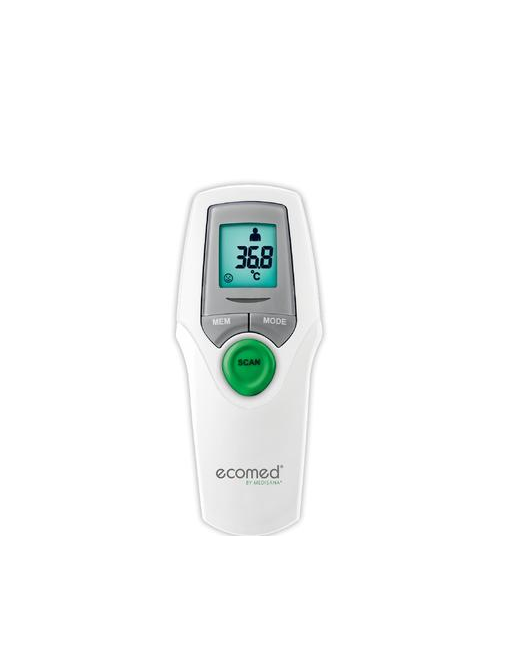
ecomed TM-65E thermomètre clinique infrarouge numérique pour bébés, enfants et adultes, thermomètre frontal, température ambiante et température du liquide : Amazon.fr: Bébé et Puériculture

Edco thermometre frontal sans contact infra rouge grundig , précis, rapide, memoire 16 temp. EDC8711252189932 - Conforama

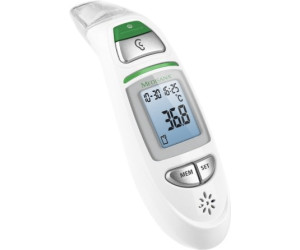
2€32 sur Medisana TM 750 Thermomètre médical avec alarme spéciale fièvre - Thermomètre - Achat & prix | fnac

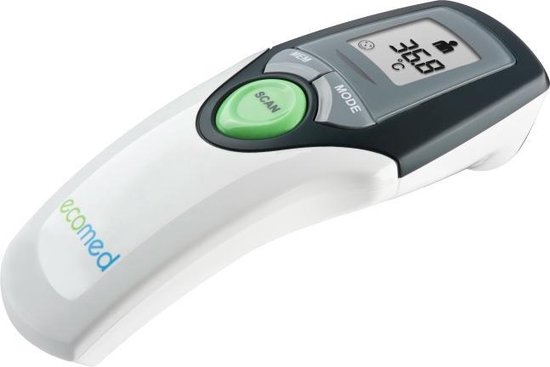
Medisana Ecomed TM 65-E au meilleur prix - Comparez les offres de Thermomètres médicaux sur leDénicheur

ecomed TM-65E thermomètre clinique infrarouge numérique pour bébés, enfants et adultes, thermomètre frontal, température ambiante et température du liquide : Amazon.fr: Bébé et Puériculture

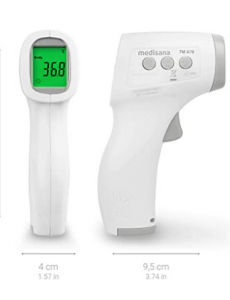
Trisa 1883.7000 Thermomètre médical infrarouge avec alarme spéciale fièvre - Conrad Electronic Suisse

ecomed TM-65E thermomètre clinique infrarouge numérique pour bébés, enfants et adultes, thermomètre frontal, température ambiante et température du liquide : Amazon.fr: Bébé et Puériculture